Introduction
Pediculosis pubis,1 caused by phthirus pubis (the crab or pubic louse), is an infestation of the hairy regions of the body, most commonly the pubic area.
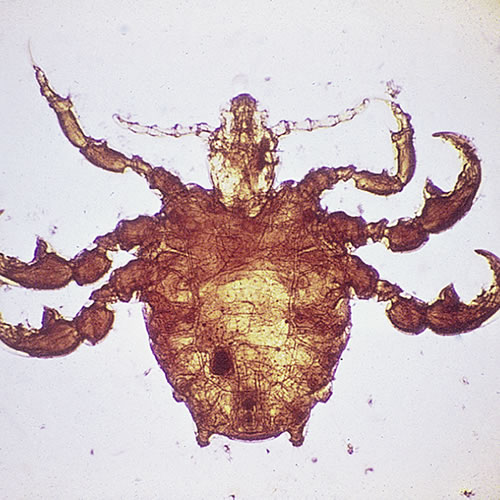
Synonyms for pediculosis are pubic lice, crabs, and crab lice.
Epidemiology
This is an infestation of teenagers and young adults, occurring equally in men and women, with the potential to infest people of all ages.
Etiology
The pthirius pubis louse lives on humans and is spread by close physical contact, either sexually or by fomites.
Symptoms and clinical features
The patient may be asymptomatic, but, usually, there is mild to moderate itching for months, involving the hairy areas of the groin but also other areas, such as the axilla, body, eyebrow, and eyelash hairs.
Small, red, primary papules (bites) may be found, but secondary changes from scratching with some serous crusts are usually more obvious. Very careful inspection reveals the 1 to 2 mm louse, attached to the base of the pubic hair. It appears as a small tan or brown speck along with the nits (eggs) attached to the lower portion of the hair shafts.
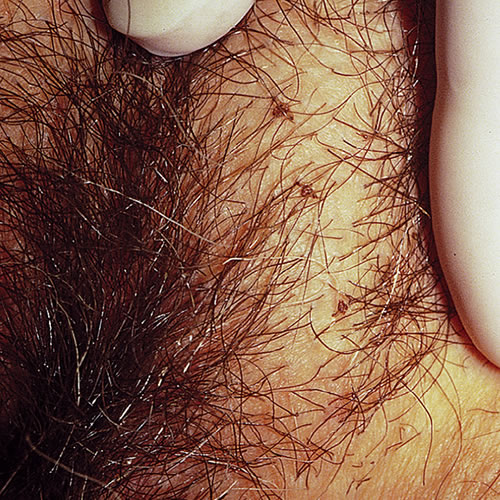
Maculae ceruleae (taches bleues), slate gray macules 0.5 to 1 cm in diameter, seen on the abdominal wall, buttock, and thigh represent louse bites, the discoloration coming from the louse saliva.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is clinical. The lice appear, grossly, as tiny brown specks. The nits look like tiny white/grey specks attached to hair.
Pathology/Laboratory Findings
The louse and the nits can be identified under a hand lens or microscope.
Differential diagnosis
Differential diagnosis includes tinea, folliculitis, scabies, and eczema.
Treatment/management
All contacts need to be treated. All personal belongings must be washed. Treatments are listed in order of preference:
- Permethrin (Nix or Rid) 1% cream rinse applied to hairy areas for 10 minutes and rinsed off. This should be repeated 1 week later, although some patients opt to shave the areas to make sure there are no nits left.
- Pyrethrins (A-200, Pronto, Tisit) applied as directed on package and rinsed off.
- Lindane 1% cream or lotion applied for 10 minutes and rinsed off or left on for 8 to 12 hours. It may be repeated, once, 7 days later.
- Petrolatum three times a day for 5 days or baby shampoo on a cotton swab three times a day for 5 days is applied to involved eyelashes.