Introduction
Fordyce spots1 are enlarged sebaceous glands that may be seen as a normal variant in the inner aspects of the labia minora and sometimes on the outer surfaces of the labia minora or peri-clitoral area. These have no relationship to apocrine gland blockage Fox-Fordyce disease.
Epidemiology
Unknown.
Etiology
Fordyce spots appear on the mucosal or transitional surfaces of the vulva in areas of ectopic sebaceous glands which do not have an actual hair follicle. In more keratinized skin, the condition presents as sebaceous hyperplasia, in which case a hair follicle is present. These are benign manifestations.
Symptoms and clinical features
Asymptomatic. The patient or her partner notices them and asks if they are normal.
The sebaceous glands on the inner aspect of the labia minora can become quite prominent, appearing yellowish, just under the skin. This is completely harmless.
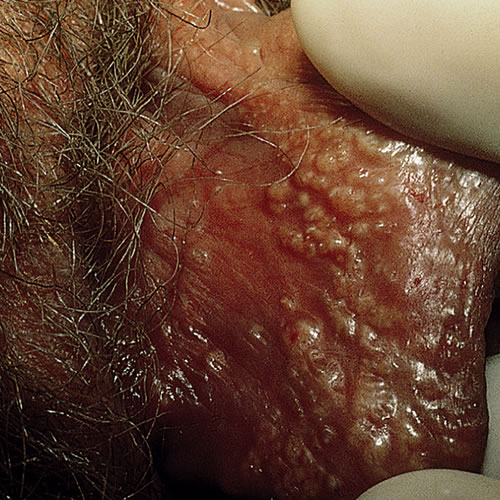
The clinician unfamiliar with this change may be concerned about missing an unusual rash or neoplasm.
Diagnosis
Once these are recognized as benign variants, they are easy to identify.
Pathology/Laboratory Findings
None needed. They will be identified as sebaceous glands if biopsy is done.
Differential diagnosis
Epidermal cysts
Treatment/management
No treatment is necessary.