Introduction
Small follicular papules and pustules result from this bacterial or fungal infection of the hair follicles.1
Epidemiology
Unknown. Very common.
Etiology
Staphylococcus aureus, Candida albicans, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa are the most common infectors. This may be seen in the vulvar area associated with shaving and waxing.
Symptoms and clinical features
Patient history involves slightly tender to itchy lesions developing in pubic hair or anywhere in the shaved vulvar area. Pseudomonas infection is associated with exposure to hot tubs.
Isolated or scattered follicular pustules with surrounding erythema are seen.
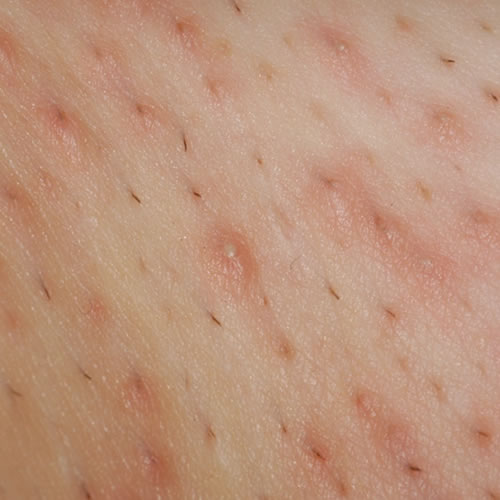
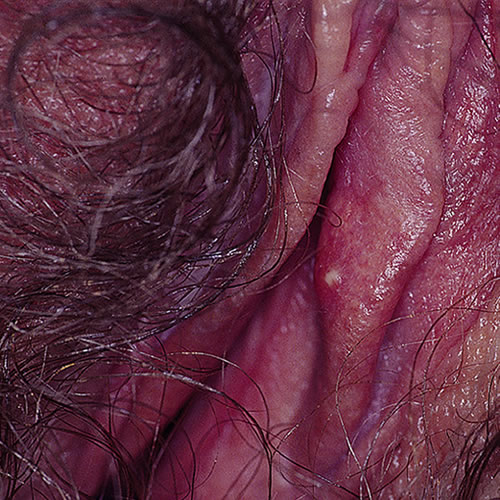
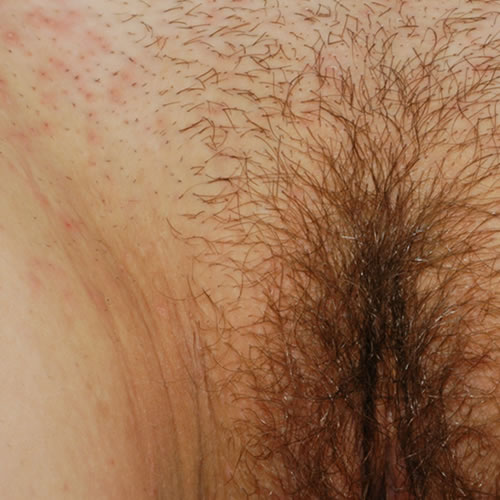
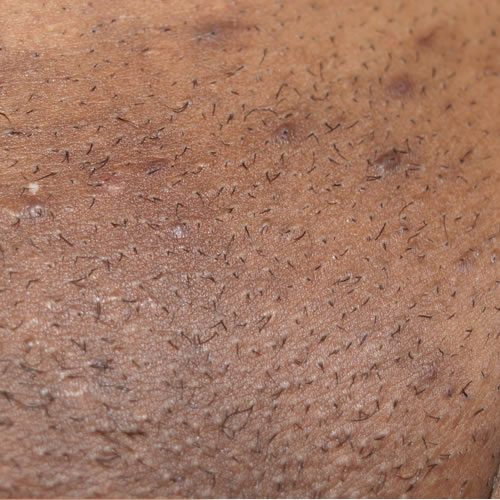
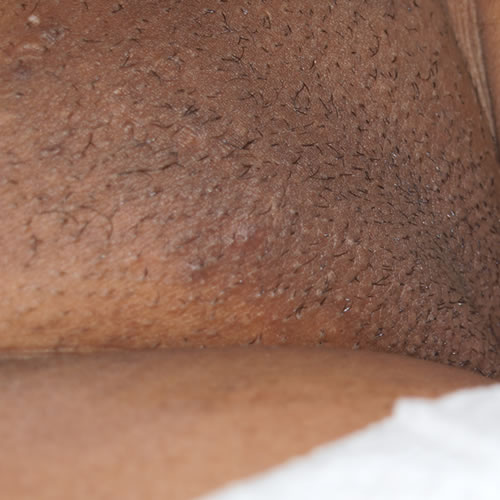
In the late stages of the infection, crusting occurs. The pustules may be formed around individual hairs.
Pathology/Laboratory Findings
Gram stain and culture confirm the offending organism. KOH wet prep can sometimes identify hyphae if fungus is involved.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis is made clinically, although culture may help to distinguish which type of organism is involved.
Differential diagnosis
Differential diagnosis includes scabies, insect bites, herpes simplex, candidiasis, and tinea.
Treatment/management
Eliminate the point of entry of the causative organism. This may involve changing techniques for shaving and hair removal.
For a few isolated lesions Clindamycin 1% topical solution twice daily and antibacterial soaps can be used.
For Pseudomonas infection, the patient’s exposure to hot tubs must be stopped. In most cases, that action alone will lead to improvement. Antibiotics may hasten improvement.
- Ciprofloxacin 250 to 500 mg orally twice daily x 5-7 days
- Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, double strength orally twice daily x 5 to 7 days
- Levofloxacin 500 mg orally once a day x 5-7 days
For Staphylococcus infection, use the following:
- Dicloxacillin 500 mg orally 4 x a day x 10 to 14 days
- Cephalexin 500 mg orally 4 x a day x 10 to 14 days
- Erythromycin 250 mg orally 4 x a day x 10 to 14 days
For suspected Methicillin-resistant staph aureus:
- Clindamycin 150 mg orally twice daily x 7-10d
- Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole DS orally twice daily for 7 days
Linezolid, Daptomycin and Tigecycline are advanced agents for rare infection resistant to the other medications.
Mupirocin cream and ointment work for the first week but resistance occurs.
Reinfection is more likely if people are carriers of staph in the nose. In these cases: Mupirocin ointment bid x 5 days applied intranasally (sometimes repeated monthly for some time) can control infection.
For yeast folliculitis resulting from Candida, use oral therapy first:
- Fluconazole or Itraconazole 100 mg orally daily x 15 days or until cleared. Use fluconazole first. (Itraconazole may be toxic.)
- Griseofulvin 500 mg orally twice daily until infection resolved. (May cause nausea and vomiting.)
- Then antifungal cream: Topical imidazole cream twice a day for 7 to 14 days (e.g., miconazole 2% cream, ketoconazole 2% cream, econazole 1% cream).