Introduction
Basal cell carcinoma1 is a tumor of the epidermal basal cells.
Epidemiology
Although it is a very common skin cancer, it is an uncommon vulvar neoplasm with a prevalence of 2.6% of vulvar neoplasms.
Etiology
There are no known predisposing factors. Ultraviolet light exposure plays a role in other areas of the skin.
Symptoms and clinical features
This is usually an asymptomatic tumor of postmenopausal women. There may be mild itching, irritation, or pain. The tumor may ulcerate and bleed with trauma.
The early lesion is a small, firm, skin-colored, pearly, asymptomatic papule (usually solitary).
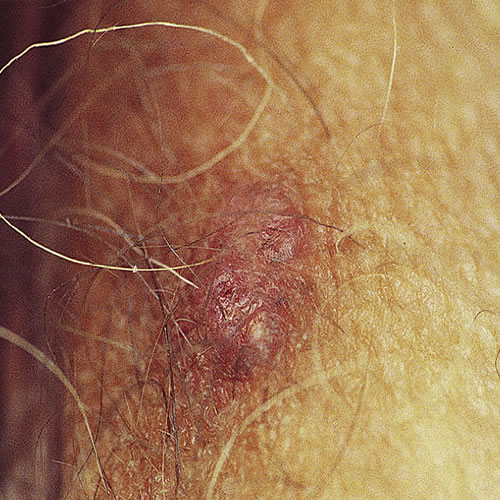
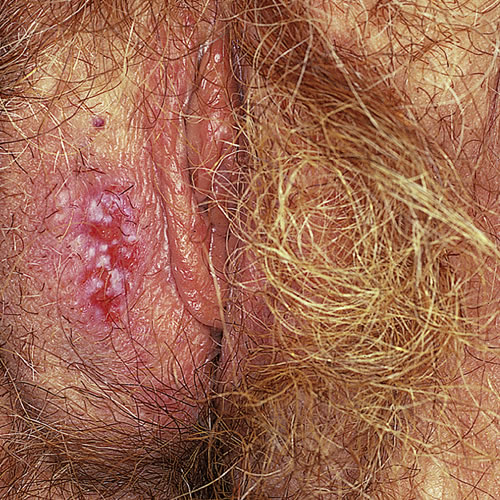
It is most frequently located on the hair-bearing area of the labium major and is more likely to be seen in older women. Pigmentation is variable. With time, the lesion ulcerates.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is made on histopathology.
Pathology/Laboratory Findings
Biopsy is needed for diagnosis, but excision is necessary for treatment.
Differential diagnosis
Molluscum contagiosum, intradermal nevus, neuroma, hidradenoma papilliferum, and squamous cell carcinoma.
Treatment/management
Complete removal of the lesions, with clear margins, is necessary. For larger lesions, surgical excision is used for removal. For lesions with questionable borders, Mohs’ micrographic surgery is best.